
Types of business process management systems Keep in mind that BPM is not a ‘set it and forget it’ strategy, as it takes ongoing evaluation to improve and adapt business processes to your organization’s current demands. From here, teams should focus on collecting data on what has gone wrong, at what stage these issues occur, or if specific employees must re-evaluate how they perform an activity.įinally, departments can shift their attention to optimizing the outlined business process.Ĭonsider all gathered information, reports and metrics when optimizing a process plan so you can make thorough improvements to efficiency. Organizations can identify new or unanticipated workflow bottlenecks during the monitoring phase. The monitoring phase of a BPM lifecycle is reserved for when management, teams and all other included stakeholders come together periodically to follow up on how a process is performing. BPM practitioners must document exactly which workflows they are changing and notify all relevant parties (customers, suppliers, employees, service providers, etc.) of all modifications to ensure business continuity. Many organizations use this part of the BPM lifecycle to test how a process would perform with smaller teams in a controlled setting. Teams can work alongside management to create a process model that highlights potential bottlenecks and possible scenarios that will arise in a pipeline.Įxecuting a process model comes after the new framework is edited, improved and ready for implementation. This depicts the beginning to the end of a task along with ways it can be optimized to deliver the best outcome. The modeling stage is the visual illustration of all steps involved in a process.
This would also be the time to take note of all the challenges that are slowing a process down.Īfter all observations are made, it’s time for the modeling phase. They would then observe the necessary documents, people, resources and further actions that are needed to reach an objective. The designing stage of a BPM lifecycle thoroughly examines how a specific process is currently carried out.įor instance, management could start by interviewing employees and teams to understand how requests are approved, claims are managed, payments are made and so on.
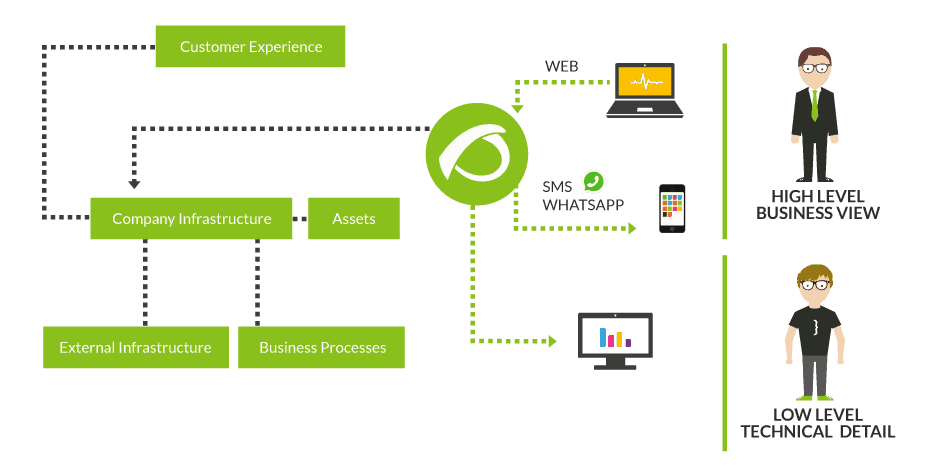
The BPM lifecycle is broken down into five stages that must be completed in sequence to achieve the desired business outcome. Understanding the BPM lifecycle is essential to deploying growth-centric strategies of your own. Compliance and risk management: Identifying legal and financial risks, notifying internal audit teams to track and resolve issues.Human Resources (HR): Onboarding new employees, automating document routing.Accounts payable and receivable: Accelerating invoice reviews and approvals, reducing late payments with visible monitoring and easier follow-ups.With BPM, organizations can streamline these activities so that their teams are able to achieve business milestones, reduce the cost of error and deliver excellent customer experiences.īPM can help organizations achieve business objectives in many different departments and functions.

The BPM discipline can be applied to operational activities that are repetitive, ongoing and predictable. The right BPM strategies allow your teams to carry out their responsibilities on time and experience faster results.īPM is the creation, optimization, implementation and evaluation of specific processes in an organization. Organizations without clear procedures will end up with operational delays, security threats and confusing processes that affect their bottom line. Business process management (BPM) is a methodology that keeps your teams efficient and your business competitive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
